Search
Explainer: What is a Gas or Vapor Explosion?
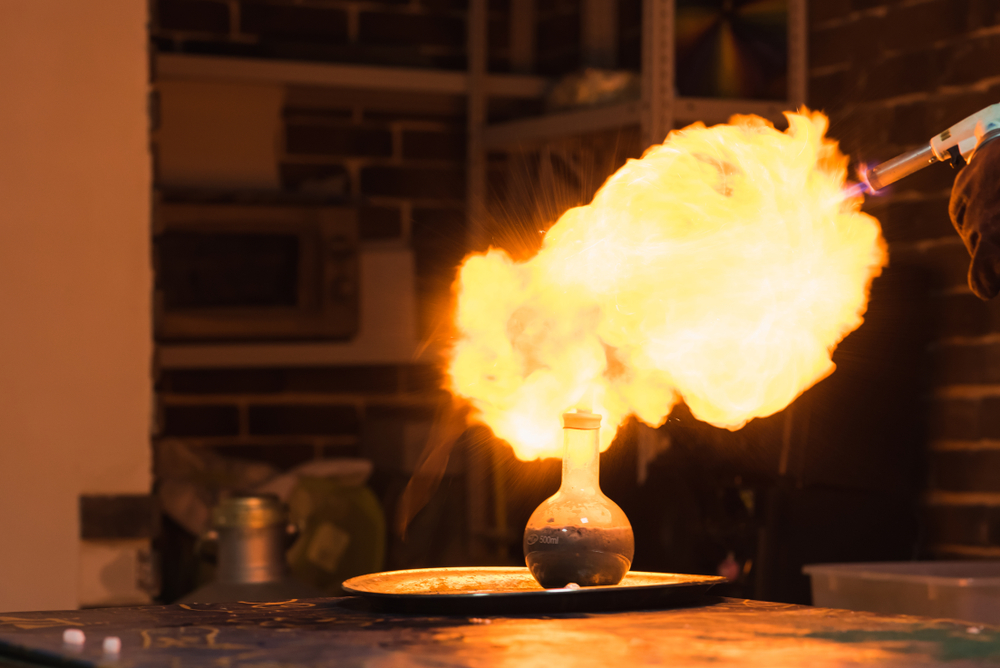

Gases or vapors, under certain conditions, can undergo a rapid combustion process known as an explosion. The primary contributors to any gas or vapor explosion are the presence of fuel, an oxidizing agent (usually oxygen), and an ignition source. Let’s break down these factors:
- Fuel: Gases such as propane, methane, hydrogen, and various volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can act as fuels. These gases contain a significant amount of stored energy in the form of chemical bonds.
- Oxidizing agent: Oxygen is the most common oxidizing agent, but other gases like chlorine and fluorine can also serve as oxidizers. An oxidizing agent is required to sustain the combustion process by providing the necessary oxygen atoms to react with the fuel.
- Ignition source: An ignition source is needed to initiate the combustion reaction. It can be a flame, impact spark, heat, electrical spark, electrostatic discharge, or any other source that provides sufficient energy to start the reaction.
When these three elements come together in a confined space and in the right proportions, an explosion can occur. Here’s a simplified explanation of the process:
- Fuel and oxidizing agent mixture: A combustible gas mixes with the surrounding air, which contains oxygen.
- Ignition: An ignition source introduces sufficient energy into the mixture to initiate the combustion reaction.
- Rapid combustion: The energy from the ignition source breaks the chemical bonds in the fuel molecules, releasing large amounts of heat. This heat further accelerates the reaction, causing the fuel molecules to rapidly combine with the oxygen molecules from the air.
- Energy release: The combustion reaction releases an enormous amount of energy in the form of heat, light, and expanding gases. The rapid release of gases generates a shockwave, which can result in an explosion if the pressure increases dramatically and rapidly.
It’s important to note that specific conditions, such as the concentration of the fuel and oxidizer, the level of confinement of the mixture, and the availability of an adequate oxygen supply, can influence the ignition sensitivity (ease of ignition) and severity of a gas explosion. A fuel air mixture that ignites in the open, creates a ‘flash fire’ whereas the same mixture igniting inside a process vessel, for example, can generate much higher pressures and can lead to rupture of the confining vessel – explosion.
In industrial settings, where flammable gases and liquids with flammable vapors are handled, stored, or transported, it is the application of good Process Safety practices that prevent these gases & vapors igniting – ensuring the protection of people, plant, and the environment.

Get in touch
To learn more about our expertise and services in dust explosion prevention & mitigation, call us at +1 609 455 0001 or email us at [email protected] today.
We also offer tailored virtual and in-company process safety training programs on Dust Explosions, Static Electricity and HAC (Hazardous Area Classification) and more. Find further information here.
We use cookies to help us enhance your experience on our website. By clicking “Accept,” you consent to our use of cookies. Read our Privacy Policy for more.